My Content
Account
Catalog
System
App & Social
Our Projects
×
![]()

{
"subject": "English",
"lang": "en",
"grade": 7,
"url_subject": "english",
"title": "English Grammar Practice: Modal Verbs Can/Could",
"description": "Exercise on using modal verbs can and could in English, focusing on ability and possibility expressions",
"keywords": ["modal verbs", "can", "could", "English grammar", "ability expressions", "possibility", "ESL exercises"]
}
Давайте разберем задание по использованию модальных глаголов can/could. 📚
1) Структура задания:
- Нужно заполнить пропуски, используя модальные глаголы can/could
- Всего 12 предложений для заполнения
2) Разбор предложений:
0) Let's buy Russian souvenirs. Shall we?
Ответ: can
(Мы можем купить русские сувениры)
1) You have never been to St Petersburg.
Ответ: could
(Ты мог бы съездить в Санкт-Петербург)
2) There are many common behaviors in different countries.
Ответ: can
(Можно найти много общего в поведении людей разных стран)
3) Let's start a new tradition.
Ответ: can
(Мы можем начать новую традицию)
И так далее для остальных предложений. При выборе между can и could учитываем:
- Can используется для выражения возможности в настоящем
- Could используется для:
* вежливых просьб
* предположений
* возможностей в прошлом
Для правильного выбора нужно понимать контекст каждого предложения и временной период, о котором идет речь. 🎯
Let's continue with the remaining sentences! 🎯
4) Come in.
Answer: can
(You can come in - expressing permission in the present)
5) There is nothing interesting for us.
Answer: could
(We could find something interesting - suggesting a possibility)
6) Use my phone.
Answer: can
(You can use my phone - giving permission)
7) Nothing can spoil these wonderful impressions.
Answer: could
(Nothing could spoil these wonderful impressions - hypothetical situation)
8) I am late for the party.
Answer: could
(I could be late for the party - expressing possibility)
9) Open the window.
Answer: could
(Could you open the window? - polite request)
10) Nobody visits that old castle.
Answer: can
(Nobody can visit that old castle - expressing ability/possibility)
11) Everybody likes holidays.
Answer: can
(Everybody can like holidays - expressing general possibility)
12) You asked nobody for help.
Answer: could
(You could ask somebody for help - suggesting a possibility)
Remember the key differences:
- Use 'can' for:
* Present ability
* Permission
* General possibilities
This exercise helps practice distinguishing between these two important modal verbs! 🌟
{
"subject": "English",
"lang": "en",
"grade": 8,
"url_subject": "english",
"title": "Travel Vocabulary and Transportation Expressions",
"description": "Comprehensive exercise on travel-related vocabulary, word combinations, and transportation verbs",
"keywords": ["travel vocabulary", "transportation", "English learning", "word combinations", "tourism vocabulary", "travel verbs", "ESL exercises"]
}
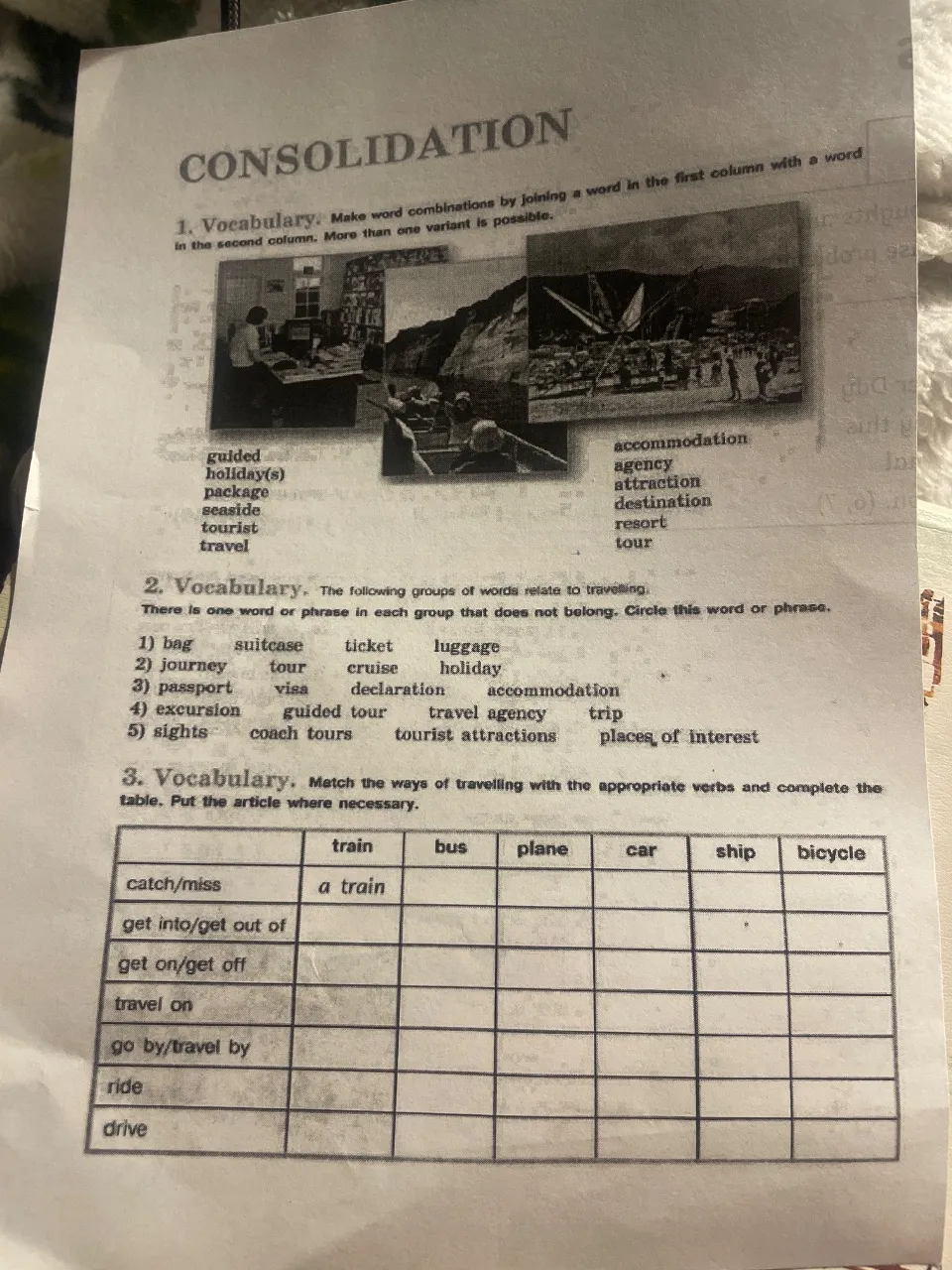
Let's solve these vocabulary exercises about travel and transportation! 🌍✈️
Vocabulary - Word Combinations
Make combinations using words from both columns. Examples:
- guided tour
- guided package
- seaside resort
- tourist attraction
- travel agency
- travel destination
Vocabulary - Odd One Out
Let's identify which word doesn't belong in each group:
1) bag, suitcase, ticket, luggage
Answer: ticket (others are containers for carrying things)
2) journey, tour, cruise, holiday
Answer: cruise (it's a specific type of travel, others are more general terms)
3) passport, visa, declaration, accommodation
Answer: accommodation (others are travel documents)
4) excursion, guided tour, travel agency, trip
Answer: travel agency (others are types of journeys)
5) sights, coach tours, tourist attractions, places of interest
Answer: coach tours (others are things to see, while this is a method of travel)
catch/miss:
- a train ✓
- a bus
- a plane
- (not used with car, ship, bicycle)
get into/get out of:
- a car
- a taxi
- (can be used with all except bicycle)
get on/get off:
- a train
- a bus
- a plane
- a ship
- a bicycle
travel on:
- a train
- a bus
- a plane
- a ship
- a bicycle
go by/travel by:
- train
- bus
- plane
- car
- ship
- bicycle
ride:
- a bicycle
- (sometimes used with motorcycle)
drive:
- a car
- (any motor vehicle)
This exercise helps understand the correct usage of transportation-related verbs! 🚗🚂✈️
Let's complete the table in detail with all possible combinations! 🚆
Here's the full completed table:
| Verb | Train | Bus | Plane | Car | Ship | Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| catch/miss | a train | a bus | a plane | - | - | - |
| get into/get out of | - | a bus | - | a car | - | - |
| get on/get off | a train | a bus | a plane | - | a ship | a bicycle |
| travel on | a train | a bus | a plane | - | a ship | a bicycle |
| go by/travel by | train | bus | plane | car | ship | bicycle |
| ride | - | - | - | - | - | a bicycle |
| drive | - | a bus | - | a car | - | - |
Important notes about usage: 🔍
catch/miss
- Used only with public transportation
- Example: "I caught the train to London"
get into/get out of
- Used mainly with enclosed vehicles
- Example: "Get into the car"
get on/get off
- Used with all forms of transport except cars
- Example: "Get on the bus"
travel on
- Can be used with all forms of transport
- Example: "I travel on trains regularly"
go by/travel by
- Universal usage with all transport types
- No article needed
- Example: "I go by bus to work"
ride
- Mainly used with bicycles and motorcycles
- Example: "I ride my bicycle to school"
drive
- Used only with motor vehicles
- Example: "I drive a car"
Remember: 📝
- Some verbs can be used in multiple contexts
- Usage might vary slightly in different English-speaking countries
- The article 'a/an' is not used with 'by' constructions
This vocabulary is essential for discussing travel and transportation! 🌟
Let me provide visual aids and a detailed explanation for both tasks.
<!-- CAN section -->
<circle cx="100" cy="80" r="60" fill="#a8e6cf" opacity="0.7"/>
<text x="70" y="70" font-size="16" fill="#333">CAN</text>
<text x="60" y="90" font-size="10">• Present ability</text>
<text x="60" y="105" font-size="10">• Permission</text>
<!-- COULD section -->
<circle cx="200" cy="180" r="60" fill="#ffd3b6" opacity="0.7"/>
<text x="170" y="170" font-size="16" fill="#333">COULD</text>
<text x="160" y="190" font-size="10">• Polite requests</text>
<text x="160" y="205" font-size="10">• Past ability</text>
<!-- Arrows -->
<path d="M150,130 L150,130" stroke="#333" stroke-width="2" marker-end="url(#arrowhead)"/>
<!-- Examples -->
<text x="20" y="250" font-size="8" fill="#666">"You can come in"</text>
<text x="180" y="250" font-size="8" fill="#666">"Could you open the window?"</text>
For the transportation vocabulary, here's a visual representation:
<!-- Central hub -->
<circle cx="150" cy="150" r="40" fill="#b5d6e0"/>
<text x="125" y="155" font-size="12">Transport</text>
<!-- Verb connections -->
<line x1="150" y1="110" x2="150" y2="50" stroke="#333"/>
<text x="160" y="80" font-size="10">catch/miss</text>
<line x1="190" y1="150" x2="250" y2="150" stroke="#333"/>
<text x="200" y="140" font-size="10">get on/off</text>
<line x1="150" y1="190" x2="150" y2="250" stroke="#333"/>
<text x="160" y="220" font-size="10">travel by</text>
<line x1="110" y1="150" x2="50" y2="150" stroke="#333"/>
<text x="60" y="140" font-size="10">drive</text>
Key points for understanding:
Modal Verbs (Can/Could):
- 'Can' is used for present situations and abilities
- 'Could' is more polite and used for hypothetical situations
- The context determines which to use
Transportation Verbs:
- Different verbs pair with specific types of transport
- Some verbs are universal (go by, travel by)
- Some are specific (drive - only for motor vehicles)
- Articles usage varies depending on the construction
The diagrams show:
- The relationship between different verb uses
- Common patterns and groupings
- Examples of correct usage
Remember to consider the context when choosing which verb or modal to use! 🎯


Use Homiwork as a regular app. It's convenient!
Add to Home ScreenUse Homiwork as a regular app. It's convenient! Open your Safari menu and tap 'Add to Home Screen'.


By starting to use the service, you accept: Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, Refund Policy
