Latin Homework Help
Okay, I will help you with your Latin homework. Let's start with the first table, "Regular Principal Parts" for the verb amo.
Задание 1: Regular Principal Parts of amo
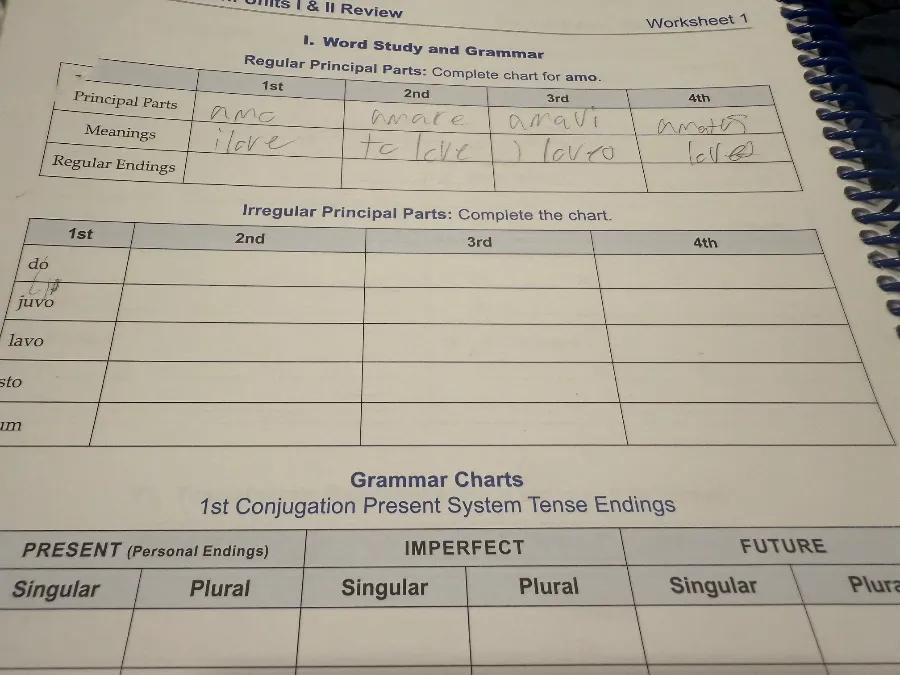
You have already filled in the table for amo, but let's review it:
| Principal Parts | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principal Parts | amo | amare | amavi | amatus |
| Meanings | I love | to love | I loved | loved |
Explanation:
- The principal parts of a Latin verb are the forms from which all other forms of the verb are derived.
- The first principal part (amo) is the first person singular present active indicative.
- The second principal part (amare) is the present active infinitive.
- The third principal part (amavi) is the first person singular perfect active indicative.
- The fourth principal part (amatus) is the perfect passive participle.
Задание 2: Irregular Principal Parts
Now, let's complete the chart for the irregular principal parts. I will fill in the missing parts for the verbs do, iuvo, lavo, sto, sum.
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th |
|---|---|---|---|
| do | dare | dedi | datus |
| iuvo | iuvare | iuvi | iutus |
| lavo | lavare | lavi | lautus/lotus/lavatus |
| sto | stare | steti | status |
| sum | esse | fui | futurus |
Explanation of the verbs:
- do, dare, dedi, datus: to give
- iuvo, iuvare, iuvi, iutus: to help
- lavo, lavare, lavi, lautus/lotus/lavatus: to wash
- sto, stare, steti, status: to stand
- sum, esse, fui, futurus: to be
Задание 3: Grammar Charts - 1st Conjugation Present System Tense Endings
Let's fill in the present system tense endings for the 1st conjugation. We'll focus on Present, Imperfect, and Future tenses. Since you didn't specify a verb, I'll provide the general endings. Remember that 1st conjugation verbs have a stem ending in -a- (e.g., amare -> ama-).
Present (Personal Endings)
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -o / -m | -mus |
| 2nd | -s | -tis |
| 3rd | -t | -nt |
Imperfect
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -bam | -bamus |
| 2nd | -bas | -batis |
| 3rd | -bat | -bant |
Future
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -bo | -bimus |
| 2nd | -bis | -bitis |
| 3rd | -bit | -bunt |
Example using amo, amare:
- Present: amo, amas, amat, amamus, amatis, amant
- Imperfect: amabam, amabas, amabat, amabamus, amabatis, amabant
- Future: amabo, amabis, amabit, amabimus, amabitis, amabunt
I have completed the first three tasks. Let me know if you would like me to continue with the rest of the exercises or if you have any specific questions about these solutions!
Okay, let's continue with the remaining grammar charts.
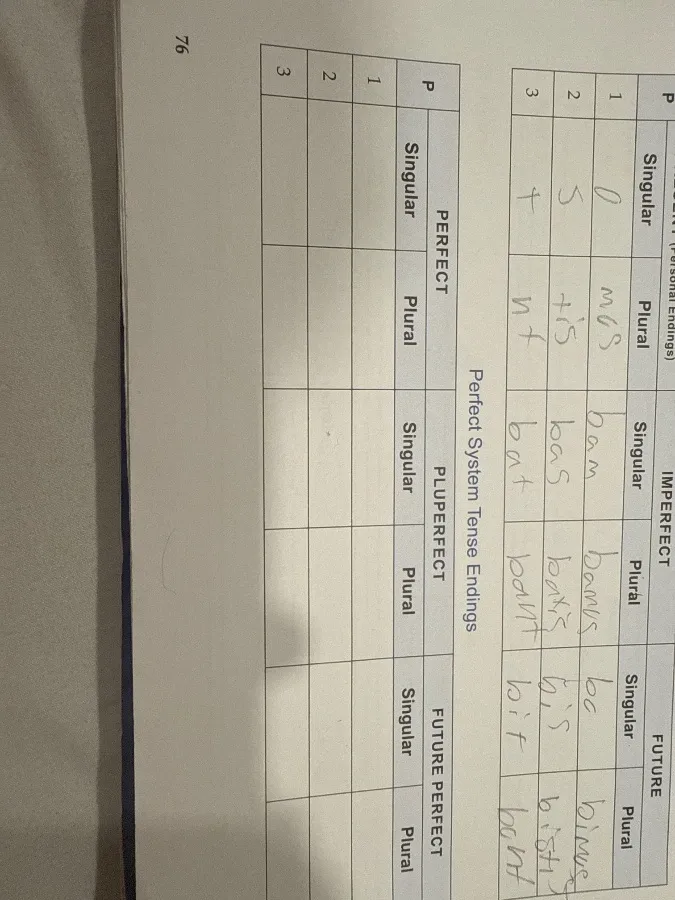
Задание 4: Perfect System Tense Endings
Now, let's fill in the perfect system tense endings. This includes Perfect, Pluperfect, and Future Perfect tenses.
Perfect (Personal Endings + Perfect Stem)
To form the perfect tenses, you take the perfect stem (usually found by removing the -i from the 3rd principal part) and add the following endings:
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -i | -imus |
| 2nd | -isti | -istis |
| 3rd | -it | -erunt |
Pluperfect
To form the pluperfect, you take the perfect stem and add the following endings:
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -eram | -eramus |
| 2nd | -eras | -eratis |
| 3rd | -erat | -erant |
Future Perfect
To form the future perfect, you take the perfect stem and add the following endings:
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | -ero | -erimus |
| 2nd | -eris | -eritis |
| 3rd | -erit | -erint |
Example using amo, amare, amavi, amatus:
- Perfect stem: amav-
- Perfect: amavi, amavisti, amavit, amavimus, amavistis, amaverunt
- Pluperfect: amaveram, amaveras, amaverat, amaveramus, amaveratis, amaverant
- Future Perfect: amavero, amaveris, amaverit, amaverimus, amaveritis, amaverint
I have completed the last task. Let me know if you would like me to continue with other exercises or if you have any specific questions about these solutions!
Okay, let's fill in the vocabulary section.
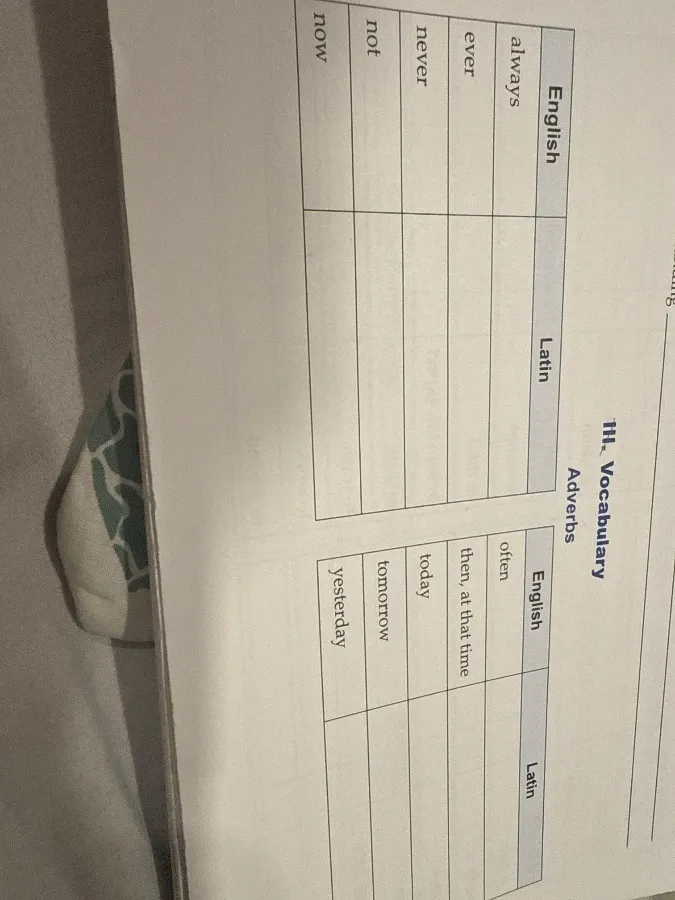
Задание 5: Vocabulary - Adverbs
Here's the completed vocabulary table with Latin adverbs:
| English | Latin |
|---|---|
| always | semper |
| ever | umquam |
| never | numquam |
| not | non |
| now | nunc |
| often | saepe |
| then, at that time | tum |
| today | hodie |
| tomorrow | cras |
| yesterday | heri |
Is there anything else I can help you with?
I understand that you're asking about helping verbs (auxiliary verbs) in Latin, specifically for forming tenses from the present through the future perfect. However, Latin doesn't use helping verbs in the same way that English does to form its tenses.
Instead, Latin relies on:
- Specific verb endings: These endings are attached to the verb stem to indicate tense, person, and number.
- Principal parts: The principal parts of a Latin verb provide the stems needed to form different tenses.
- Different verb stems: Present, perfect, and future stems are used to build different tenses.
Here's a breakdown of how tenses are formed without auxiliary verbs:
-
Present System:
- Present: Formed from the present stem (usually the 2nd principal part minus -re). Add personal endings.
- Imperfect: Formed from the present stem + -ba- + personal endings.
- Future: 1st and 2nd conjugation: present stem + -bi- + personal endings. 3rd and 4th conjugation: present stem + -e- or -a- + personal endings.
-
Perfect System:
- Perfect: Formed from the perfect stem (usually the 3rd principal part minus -i). Add perfect personal endings.
- Pluperfect: Formed from the perfect stem + -era- + personal endings.
- Future Perfect: Formed from the perfect stem + -eri- + personal endings.
-
Passive Voice:
- Latin uses the verb sum, esse, fui, futurus ("to be") as an auxiliary verb to form the passive voice in the perfect, pluperfect, and future perfect tenses. For example: amatus est (he has been loved).
Example:
Let's take the verb laudo, laudare, laudavi, laudatus (to praise).
- Present: laudo (I praise)
- Imperfect: laudabam (I was praising)
- Future: laudabo (I will praise)
- Perfect: laudavi (I have praised)
- Pluperfect: laudaveram (I had praised)
- Future Perfect: laudavero (I will have praised)
In summary, Latin doesn't use helping verbs to form active tenses in the same way as English. Instead, it relies on specific endings and stems. The exception is the use of sum to form passive tenses in the perfect system.
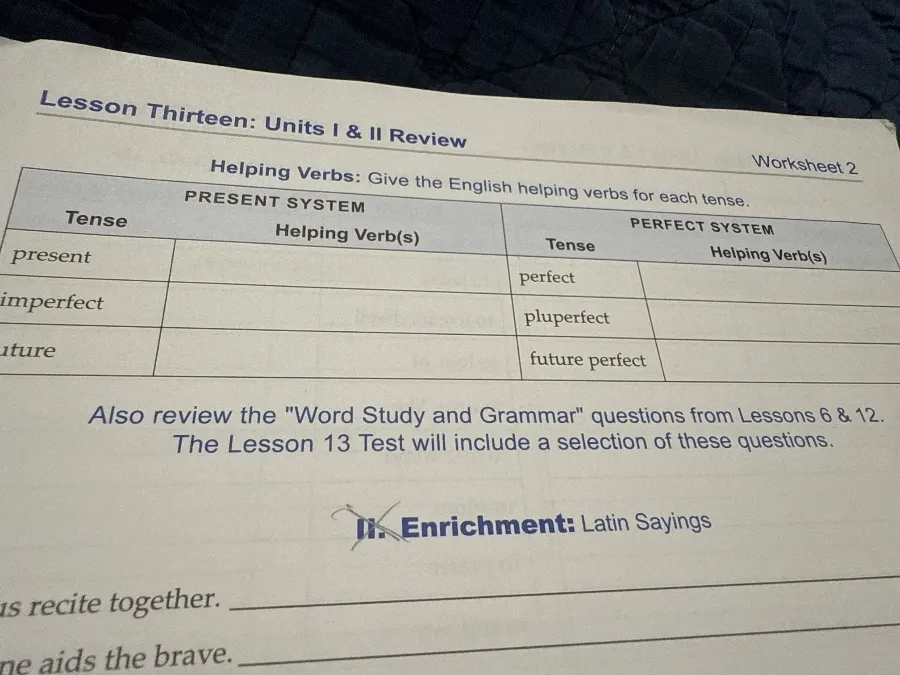
Ассистент: Okay, I understand your question now. You're asking about the English helping verbs that correspond to the Latin tenses. Here's the table filled in with the appropriate English helping verbs:
Задание 6: English Helping Verbs for Latin Tenses
| Tense | Helping Verb(s) |
|---|---|
| Present System | |
| Present | (none) / is, are |
| Imperfect | was, were |
| Future | will, shall |
| Perfect System | |
| Perfect | has, have |
| Pluperfect | had |
| Future Perfect | will have, shall have |
Explanation:
- Present: In English, the present tense often doesn't require a helping verb (e.g., "I love"). However, with certain verbs, we use "is" or "are" (e.g., "He is running").
- Imperfect: The imperfect tense in Latin often translates to the past continuous in English, which uses "was" or "were" (e.g., "I was loving").
- Future: The future tense in both Latin and English uses a helping verb to indicate future action. In English, this is typically "will" or "shall" (e.g., "I will love").
- Perfect: The perfect tense in Latin corresponds to the present perfect in English, which uses "has" or "have" (e.g., "I have loved").
- Pluperfect: The pluperfect tense in Latin corresponds to the past perfect in English, which uses "had" (e.g., "I had loved").
- Future Perfect: The future perfect tense in Latin corresponds to the future perfect in English, which uses "will have" or "shall have" (e.g., "I will have loved").

Okay, I'll help you with the remaining tasks.
Задание 1: Form Drills - filimus
- Translation: We spin
- Person: 1st
- Number: Plural
- Tense: Present
Задание 2: Form Drills - erimus
- Translation: We will be
- Person: 1st
- Number: Plural
- Tense: Future
Задание 3: Form Drills - narravit
- Translation: He/She/It told
- Person: 3rd
- Number: Singular
- Tense: Perfect




